Search engine optimization (SEO) is an integral part of a successful online marketing strategy.
By understanding and implementing SEO techniques, you can enhance your website's chances of appearing higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) and driving more organic traffic to your site.
SEO involves an entire ecosystem of practices, so it's natural to feel a bit overwhelmed when you first encounter it.
This guide clears the air and teaches you everything you should know and do to execute a high-performing SEO strategy.
What you will learn
- What SEO is and why it matters
- The criteria search engines use to decide which pages earn top spots in search results
- The different SEO strategies and techniques
- How to measure and improve your website's SEO standing
What is search engine optimization (SEO)?
SEO is a set of practices that improve a web page's visibility in search engine results.
These practices are primarily aimed at boosting your Google search rankings. Generally, they also apply to other search engines, such as Bing and Yahoo .
The main goal of SEO is to secure a high rank in organic search results, which are unpaid listings determined purely based on search algorithms.
By contrast, paid results are obtained through paid ads and are prominently displayed in SERPs, with the exact position depending on an entirely different set of factors.
For clarity's sake, here's the difference between an organic and paid search result in Google:

As you can see, the first result has the Sponsored mark above it, which indicates a paid result. The other article ranks organically in the top spot for such a query.
Why is SEO important?
SEO makes it easier for users to find your content among thousands of competing pages. This ensures abundant organic traffic and plenty of leads for your business, which can turn into customers with the right content marketing funnel.
Simply put, SEO is a gift that keeps giving—once your page ranks high, you get a stable, long-term stream of leads and buyers.
SEO also does wonders for brand awareness and setting yourself apart from the crowd. If Google sees your website as a valuable resource that users keep returning to, it'll send more people your way. Your influence and authority will grow with time, letting you secure a prime spot in your niche.
Suppose you're wondering why we keep focusing on Google despite saying SEO also applies to other search engines.
In that case, there's a simple reason—it's undoubtedly the most popular search engine, with a market share of over 81%.
Google processes over 40,000 searches every second, which speaks volumes about the importance of improving your visibility in Google SERPs.
And if you're thinking about taking a shortcut and simply paying for a sponsored result, think again—a report by FirstPageSage showed that the highest-placed paid result had a click-through rate (CTR) of only 2.1% compared to a whopping 39.8% for the first organic result.
While there's certainly a time and place for paid ads, nothing beats a high organic rank.
It's far more viable in the long run, as you don't need to keep pouring money into your SERP placement.
How search engines work
Search engines perform three tasks before a user can see a page in SERPs:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Ranking and serving search results
Once Google discovers a URL, it crawls the page to see what it includes. This is done through crawlers, also known as bots, robots, or spiders.
Google then indexes the page, closely examining its text, visuals, metadata, and other elements. When this process is over, the page is added to Google's index—a massive library of web pages from which the search engine draws to present search results.
Note that crawling and indexing may not always happen as intended. Some of the main issues that prevent Google's bots from doing their job include the following:
- Server or network issues
- robots.txt rules prohibiting access to the page
- Poor content quality or page design
Duplicate content can also be the reason a page isn't indexed. One of the main goals of indexing is to identify the so-called canonical page and weed out alternate/duplicate pages. If your website has pages with the same or similar content, you can use canonical tags to define the original version and make sure it's not overlooked.
You can see which of your pages are indexed by going to the "Indexing" tab in Google Search Console. Alternatively, you can perform a Google search for site:[website name], like so:

If some important pages weren't indexed, you can submit an indexing request through Google Search Console.
In some cases, you'll want to do the opposite and prevent a page from being indexed. For example, if you have an old blog post you're yet to update, you can prevent its indexing by adding the noindex meta tag to the page's HTML.
When your pages are added to Google's index, they're matched to a user's query and ranked in the search results according to hundreds of factors. The good news is that many of those factors are under your control, so you can do a lot to get your page ranked high.
The basics of SEO
SEO involves a wide range of practices, though you don't need to know about all of them immediately. Let's focus on a few fundamentals to get you started on the right foot.
Keyword research
While search engine algorithms use many factors to determine a page's rank, keywords are the heart and soul of every SEO strategy.
The goal of keyword research is to find relevant search terms for your business and include them in your content. Doing so lets you connect your pages to relevant search phrases so that Google can serve them in SERPs.
The keyword research market is massive, so countless tools exist to explore. Still, if you're learning SEO from scratch, you might want to focus on free platforms until you get the hang of the research process to avoid overpaying for advanced options.
You can start exploring your target keywords using Google's features like autocomplete. Start by entering a search term relevant to your niche, and see what comes up. You'll get various suggestions, like so:

The bolded phrases show related searches, which you can use as long-tail keywords in your content. You can uncover more potential keywords and topics by going to the People also ask section of the SERP, as shown in this image:

You'll want to go beyond the above suggestions, as the goal is to find as many relevant keywords as possible.
You can broaden your search using Keyword Surfer—our free Chrome extension that gives you many keyword ideas directly in the SERPs.

When deciding which keywords to use, focus on a few key metrics:
- Monthly search volume
- Keyword relevance
- Ranking difficulty
To assess the above, you can rely on Surfer's keyword research.

As a rule of thumb, you'll want to avoid highly competitive keywords initially.
Otherwise, you'd be up against well-established websites with many backlinks and accumulated authority.
Choose keywords that balance search volume and ranking difficulty.
As your website grows, you can tackle the tougher ones.
Another crucial element of successful keyword research is identifying the right search intent. There are four types of intent:
1. Informational—The user is looking for information about the topic ("What are TWS headphones?")
2. Navigational—The user wants to reach a specific website ("TWS headphones Reddit")
3. Commercial—The user is considering buying a product and is comparing different options ("JBL vs. Sennheiser TWS headphones")
4. Transactional—The user is looking to purchase the product ("JBL TWS headphones price")
Each page must meet the search intent, meaning you need to use the right keywords and content types.
For example, keywords with commercial or transactional intent are perfect for landing pages, while informational keywords are good for high-level guides.
Google cares a lot about helping users meet their search intent, so do not overlook it.
SEO content
As mentioned, the keywords you find will be placed all over your website through different types of content. Well-optimized web copy, blog posts, and other content forms are crucial for ranking high, so most of your SEO efforts will be focused on them.
Now, it's not enough for your web page to include all the relevant search queries—it must be genuinely helpful to the reader if you want Google to single it out among tons of other pages.
With that in mind, you need to create people-first content that still checks all the relevant search algorithm boxes.
Striking this balance is no easy feat if you're just starting out with SEO, but it's more than doable with some practice. Here are some useful tips to get you started:
- Put yourself in your audience's shoes—When writing a content piece, consider your readers' perspective and ask yourself what they want to know about the topic.
- Avoid keyword stuffing—Don't overfill your content with keywords, as Google will see this as an attempt to manipulate search rankings, which is bound to backfire. Use all keywords naturally throughout the text, ideally so that an average reader won't even notice them.
- Create compelling headlines—Eye-grabbing title tags and H1 tags are crucial for maximizing the click-through rate, a major ranking factor, and engaging the reader. Make sure they include the primary keyword and power words ("Ultimate Guide," "Proven Ways," "Actionable Tips," etc.), but avoid clickbait titles that overpromise.
- Proofread and edit your content—Whenever you finish a content piece, give it a read-through to eliminate grammar and spelling mistakes. More importantly, cut out all the fluff you might notice to make the piece as valuable as possible.
Creating high-quality SEO content takes time and skills.
The good thing is that nowadays, you can rely on several SEO and AI tools to help you with it.
For instance, with Surfer AI you can have a fully optimized article ready in less than 20 minutes. This would otherwise take hours of research, planning, and drafting.
.gif)
What's left is for you to humanize the AI content draft:
- Add personal anecdotes or experiences.
- Use natural, conversational language.
- Include humor or relatable examples.
- Edit for tone and style consistency.
- Incorporate real-life case studies or testimonials.
- Use Surfer's free AI Humanizer

User experience
SEO success is determined not only by the value your content provides but also by its structure. If the user has trouble navigating or reading your piece, they'll go back to the search results quickly, regardless of how informative or useful it is.
In other words, you'll have a high bounce rate—the percentage of unengaged sessions where the user opens a page and returns to SERPs without visiting other pages on the website.
The higher your bounce rate, the less relevant or useful your pages will be in Google's eyes.
To avoid this issue, pay close attention to the user experience (UX) when structuring the page. Specifically, follow these tips to format your content properly:
- Avoid huge blocks of text—If your page has large black-and-white chunks, the reader is bound to get bored and even tired of reading. Use bullet points, images, lists, quotes, and other elements to make your content skimmable and dynamic.
- Organize the page with headings—In addition to the H1 tag you'll use for the title, leverage other heading tags to break up your text and create a logical structure.
- Maximize readability—You might feel compelled to add complex terminology to appear more authoritative, but resist this urge unless you're writing academic pieces. Use plain language and simple sentence structures to make your content readable.
- Use enticing CTAs—Avoid generic CTA like "click here" and "visit this page," as they'll most likely get ignored. Make your CTAs compelling by using visuals and making them feel personal.
So, what do the above tips look like in practice? A perfect example is Diet Doctor's keto diet article. The following section alone checks many important UX boxes:
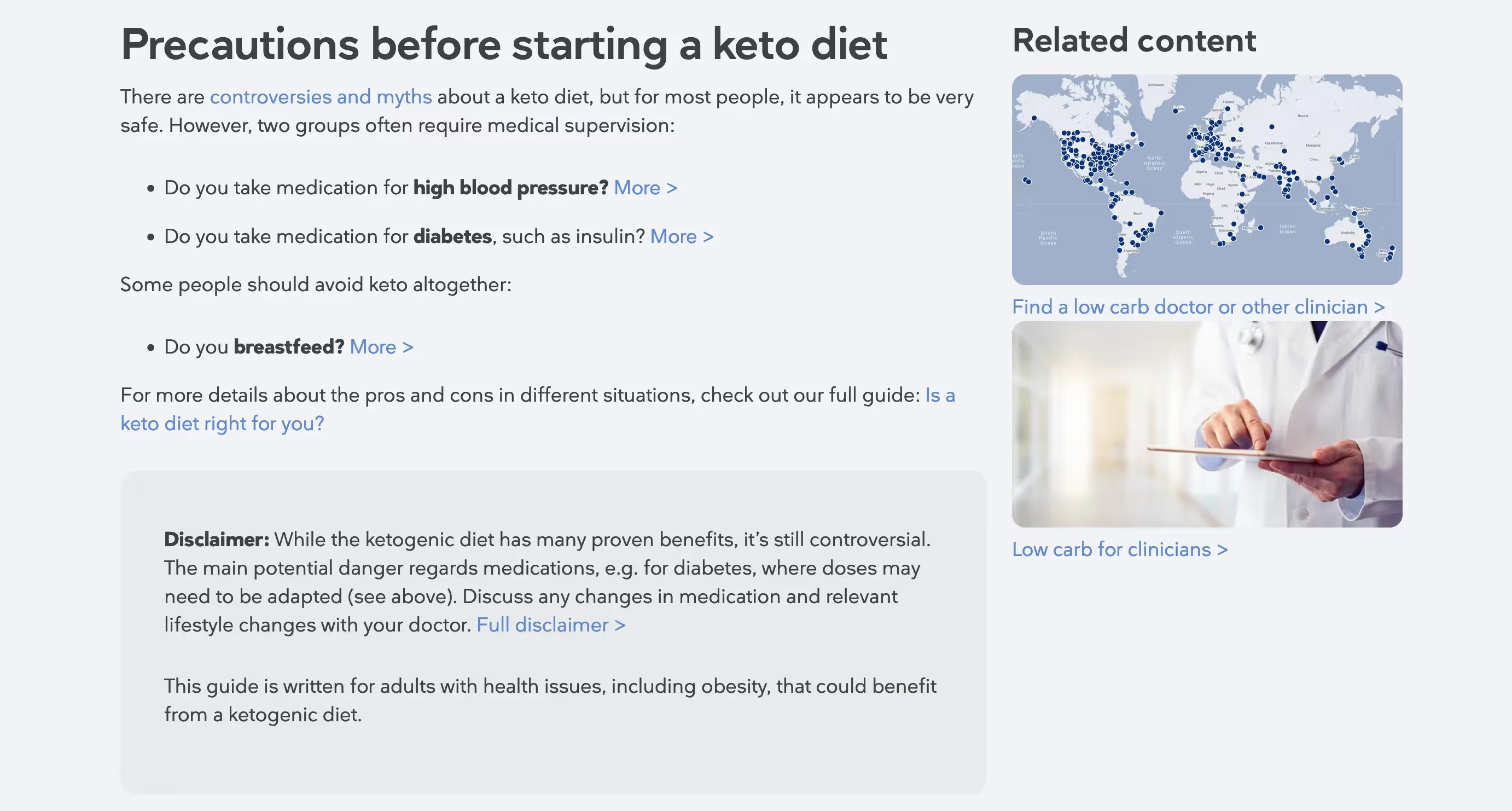
The page doesn't feel too busy or monotonous and is easily skimmable thanks to bullet points and bolded sections. There are also links to other useful content, which can reduce the bounce rate by compelling the reader to click through.
As for the CTA, it perfectly encompasses everything we explained above, as you can see here:

Instead of simply saying, "Click here to get a free trial," the CTA immediately draws the reader in by asking for their gender so that they can get a personalized meal plan. Follow the same method of understanding your readers and their pain points, and your CTAs will be highly effective.
On-page SEO
Besides a page's content, you need to optimize several key elements that help search engines understand what the page is about, most notably:
- Title tags—Not to be confused with an H1 tag, a title tag defines your page's headline in SERPs, social shares, and link previews.
- Meta descriptions—A meta description is a short summary of a page that tells the reader and Google's crawlers what they can expect on the page.
- Heading tags—As mentioned, heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) break up your text and make the article more skimmable and easy to crawl.
- URLs—A well-optimized URL ensures consistency and page relevance in the eyes of Google's crawlers.
Making these elements SEO-friendly isn't hard—it all comes down to a few small but important steps. Firstly, you should include the primary keyword in the title tag, meta description, URL, and H1 tag. Here's an example of how we did it for our article on keyword research tools:

In the above image, you can see the keyword implemented in the title tag and meta description. Here's what it looks like in the URL and H1:

You'll most likely have various secondary keywords, which you can place in other heading tags as long as you do it naturally without forcing the keyword in.
You can find relevant keywords to include in your article in Surfer's Editor.

As Google crawls your page and sees relevant keywords used contextually, it'll deem your article more valuable for the given search query.
Alternatively, you can let Surfer's Auto-optimize feature do the on-page optimization for you. Surfer will analyze your content and insert important terms in a contextually relevant way.

Besides keywords, you should pay attention to the length of your metadata. Make sure not to exceed the following values:
- Title tag—up to 60 characters (including spaces)
- Meta description—140–160 characters
Note that your title tag can be similar or even the same as the H1 tag. The only thing that matters is that it's not too different because this can harm the page's consistency and confuse search engines.
Internal linking
As the name implies, internal links connect pages within your website instead of sending the reader away from it. By linking relevant pages together, you'll check three important boxes:
- Creating a clear site structure
- Reducing bounce rate and improving time on site by guiding readers through several content pieces
- Making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your pages
Like other aspects of search engine optimization, internal linking has a few important rules you should follow, most importantly:
- Always link to related or complementary content to avoid random connections that confuse readers and search crawlers.
- Use descriptive anchor text relevant to the destination page instead of placing naked links or using generic anchors like "click here" or "read more."
- Avoid repeating the same anchor text for different links on a page.
- Link from high-authority pages with a lot of search traffic to the lower-performing pages to pass on link equity to them.
- Avoid link stuffing to maintain a clear structure of your pages.
As you blog grows, it may be more difficult to keep track of which pages to link to. That's not the case when you're using the Surfer Editor.
From within the Content Editor you can see the Insert internal links feature. Surfer will scan your domain and automatically insert internal links in relevant parts of your article, using proper anchor text.

Link building
Link building is the practice of getting authoritative and reputable websites to link to your pages. It's a vital aspect of off-page SEO, which is equally important as on-page optimization.
The idea behind link building is simple—the more reputable sources send users to your website, the more authoritative Google will see it.
As a result, your pages will seem more credible and be placed higher in SERPs.
This won't happen overnight, as building links takes time. Here are some of the best ways to get started:
Tap into existing connections—If you have some connections in your niche, you can partner up with them through collaborations, interviews, and other tactics to get you a link from their website.
Use guest posting—Many websites let you publish articles on their website as a contributor and add links to your pages. To find guest posting opportunities, Google your niche with relevant keywords like "write for us," "guest posting," and "submission guidelines."
Leverage HARO—HARO stands for Help A Reporter Out, and it's a program where you can sign up as a source of information for journalists. When you make a contribution, they'll cite you as a source and link to your website.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on factors a user might not see, but that still impact their experiences, such as website security, site architecture, and page speed.
Search engines are all about ensuring an overall pleasant experience, so addressing these factors is crucial for climbing SERPs.
If you need an example of why this is the case, just look at how page speed affects the site's bounce rate.
One study found that if your website loads within two seconds, the bounce rate is only 9%. But if a page takes 5 seconds to load, it jumps to 38%.
There are many ways to reduce page load time, but the most beginner-friendly one is to compress heavy elements like images and videos. They're often the ones bogging down a page the most, so reducing their size by even a little can have a massive impact on your page speed.
Now, page speed is only one of the many technical SEO basics to focus on. Here are some additional tips you'll want to follow:
- Check robots.txt—robots.txt tells search engines which pages of your website should and shouldn't be crawled. You can find it by entering a site's URL followed by "/robots.txt." You can then download the file and edit it to ensure all important pages are crawlable. Many content management systems (CMS) make it easy to edit and upload your robot.txt file, so the process shouldn't be too complex.
- Optimize Core Web Vitals—Google outlines three Core Web Vitals you should know about:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)—The time necessary to load the largest content element in the viewport
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP)—The measure of a page's overall responsiveness to a user's interactions
- Cumulative Layour Shift (CLS)—The sum total of all unexpected layout shifts on your page
- Optimizing these elements can drastically improve several technical SEO metrics, so head to Google Search Console to find a Core Web Vital report and look into them.
- Other things you can focus on in terms of technical SEO are:
- Set up HTTPS—Domain security is an important ranking factor, so ensure your website has an SSL certificate and a configured HTTPS protocol.
- Make your website mobile-friendly—Around 63% of all searches happen on mobile devices, so it is not surprising that Google shifted to mobile-first indexing in 2023. Optimize each web page for mobile users to avoid losing traffic and SEO points.
Local SEO
If you run a local business, one of the best ways to improve its visibility and secure a good placement in search engines is to focus on local SEO.
Specifically, you should create and optimize a Google Business Profile page that will be displayed prominently in SERPs, like so:

Once you sign up for Google Business Profile, you'll be listed in the Local Map Pack but might not be featured among the top three local businesses straight away. To maximize your chances of being in the top results, follow these tips:
- Use your actual business name and provide all the relevant details (working hours, phone, address, etc.)
- Upload high-quality images
- Write an engaging description, and use the right keywords in it (without keyword stuffing)
- Encourage positive reviews
Another important component of local SEO is the consistency of your NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) citations. They appear on other websites and lead back to your business, and it's essential to make sure all your NAP data is the same across those websites.
You can use tools like BrightLocal's Citation Tracker to monitor your NAP citations and ensure consistency.
SEO tools
SEO can be pretty overwhelming at first, but don't worry—you don't need to do it all on your own. You can leverage countless tools that handle the heavy lifting and let you focus on decision-making. Whether you want to check a page's keyword rankings, get backlinks, or examine other sites to see what the competition is doing, there's a platform that can help.
Here are some of the most popular SEO tools you'll want to check out:
- Surfer—Great for overall SEO, from keyword research to content strategy and audits. With Surfer, you can also create SEO-friendly content at scale by leveraging the power of AI.
- Google Analytics—A free, easy-to-use tool that helps you understand and improve your search traffic.
- Screaming Frog—A handy tool that simulates Google's crawling process and lets you work on your website's technical SEO.
- Google Search Console—A free tool that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your website's presence in Google Search results.
You can use these tools as a starting point and explore more as your SEO strategy evolves.
Measuring SEO performance
As you go about checking all of the boxes you've seen in this guide, you'll want to have a firm grasp on what works and what doesn't. SEO involves initially experimenting until you've figured out the nuts and bolts.
That's why you should monitor the performance of all your tactics continuously. You can use tools like Google Search Console and Google Analytics to do this, as they let you track some of the most important metrics, such as:
- Click-through rate
- Impressions and clicks
- Bounce rate
- Search traffic
- Key search queries
- Audience demographics
You can also leverage third-party tools, such as Surfer's SEO Audit, which lets you effortlessly assess and optimize your existing content.
Track your pages' performance over time, and experiment with different tactics until you find what works.
How to learn SEO
While this guide touches on all the key aspects of SEO, you'll need to dive much deeper to grasp it fully. Luckily, there are countless free sources you can turn to for help, such as:
- Surfer's blog
- Google Search Central
- YouTube channels (Ranking Academy, Craig Campbell SEO, etc.)
- Official sources and guidelines from search engines (e.g., Google's list of updates)
The SEO landscape evolves at all times, so you should check the above sources frequently to stay updated on all the relevant changes.
You can also look for courses that let you build specific skills, such as Surfer's SEO Writing Masterclass, which teaches you everything you should know about creating content that ranks high in SERPs.
Still, no theoretical knowledge beats hands-on experience.
You'll inevitably go through a trial-and-error phase, which is perfectly normal and even necessary for becoming a pro.
Make sure to apply your knowledge as much as possible, and give yourself time to master all the intricacies of SEO.
Key takeaways
- Search engine optimization is critical for driving organic traffic and leads to your website. It enhances your online visibility and is a valuable long-term investment.
- Search engines crawl, index, and rank pages based on numerous factors. Knowing how this process works helps you optimize your website effectively.
- Identifying and using the right keywords is the backbone of any successful SEO strategy. Target keywords that balance search volume and competition.
- Content should be people-first, engaging, and informative. Avoid keyword stuffing and focus on delivering value to your readers.
- Ensure title tags, meta descriptions, heading tags, and URLs are SEO-friendly and include relevant keywords.
- Use internal links to create a clear site structure, reduce bounce rates, and make your content easier to crawl.
- Acquire links from authoritative and reputable websites to boost your site's credibility and search engine ranking.
- Optimize page speed, mobile-friendliness, and other technical aspects to improve user experience and search engine rankings.
- For local businesses, optimizing Google Business Profile and maintaining consistent NAP citations can significantly enhance local search visibility.
- Utilize tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and Surfer to streamline your SEO efforts and make data-driven decisions.
- SEO is an ever-evolving field. Stay updated with the latest trends and best practices through blogs, courses, and official search engine guidelines.
Conclusion
Rising to the top of SERPs is no easy feat, but it's more than possible with time and a few smart moves. Now that you've gotten the hang of SEO fundamentals, it's time to take the first steps and prepare your pages for ranking.
Using the right tools, you can take many shortcuts. Nevertheless, SEO is a long game. Don't expect overnight results, and keep tweaking your strategy as needed.
All the effort will be worth it when you see your pages on the first page of Google.


.avif)
