Google Search Console (GSC) is an excellent SEO tool to optimize your website for SEO. It provides a wealth of data and insights that can help you improve your rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs).
While third-party research tools can be useful, using your website's Google Search Console account will help you quickly identify existing opportunities for increased organic search traffic.
In this guide, I'll show you step-by-step how to use Google Search Console for search engine optimization and keyword research. You'll also learn how to use its most common reports and some advanced Search Console hacks.
How to use Google Search Console for SEO
The data in Google Search Console can help you track your website's performance in Google's organic search results and identify opportunities for improved rankings and traffic. GSC has several valuable reports we'll walk through later in this article.
Note: If you're new to GSC, ensure that you verify site ownership and set up Google Search Console for your website first.
Note: Learn how to enter and submit an XML sitemap URL in Google Search Console here.
How to use Google Search Console for keyword research
The queries data in Google Search Console's Search results report can be beneficial for identifying search terms that your website's indexed pages show up for in the SERPs. Queries tell you which existing keywords readers use to find your pages so you know which keywords to focus your keyword optimization efforts on.
However, the report in Search Console doesn't tell you anything about which new keywords and topic ideas your website should create blog posts for. Or the search volume and traffic that these keywords receive. Instead, I use Surfer's keyword research tool to help me identify new topic ideas based on keywords I'm already ranking for, along with their search volume information.
Follow these steps to use Google Search Console's data for keyword research.
- Open Surfer Keyword Research
- Enter your target keyword and country
- Click Create Keyword Research
Note > If you need help entering a target keyword, head to Google Search Console > Performance > Search results > queries and pick a broad keyword you rank for.
Surfer will take a moment to generate a list of new keyword clusters grouped by the main topic. But before you go any further, ensure that this data is personalized for your website by connecting your Google Search Console account.
Click on the Google icon on the right-hand side and follow the instructions.

Connect the domain you want to use GSC data for.
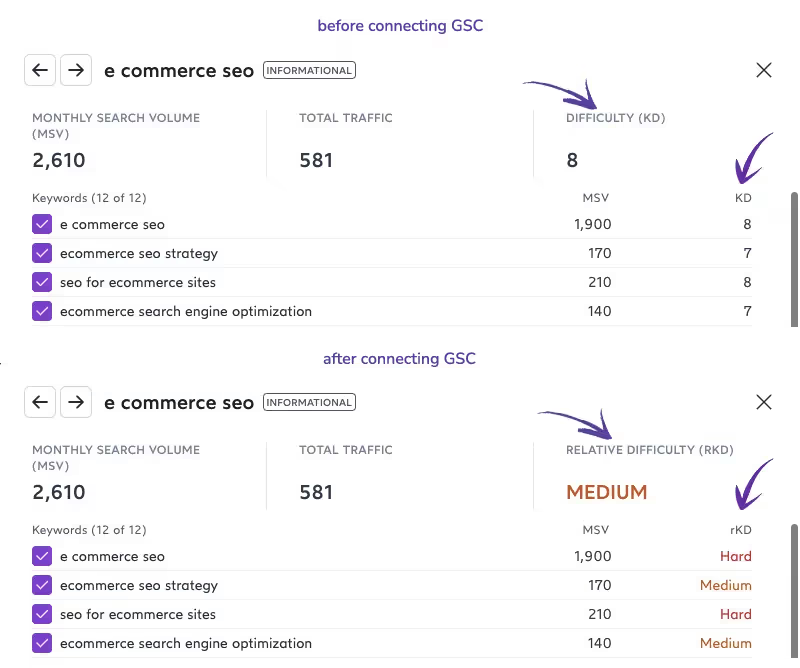
The Google icon will display a green dot instead of a black one in a couple of seconds. And you'll immediately see the difference in results from the Keyword Research tool. So, for example, Surfer will show you relative keyword difficulty (RKD), a rating based on your GSC data instead of just keyword difficulty (KD) which is a generic rating based on the SERPs.
You'll also notice that the rating is now personalized to your website's relative authority on that topic reflected on a scale of easy-medium-hard compared to the previous scale of 1-10. In addition, Keyword Research will also show you the monthly search volume and total traffic you can expect to attract by ranking for these keywords.
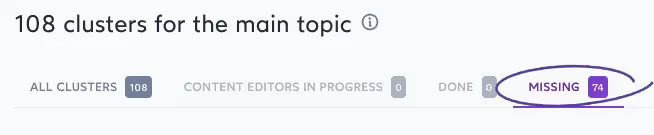
Another advantage of connecting GSC data with Surfer Keyword Research is to uncover missing topical clusters on your blog that will help you establish authority. A new tab, Missing, will show you opportunities you're missing out on.
For example, I'm missing 74 of the recommended topic clusters for a blog in my niche. Creating content on these topics will help my blog increase traffic and earn authority in the eyes of search engines, thus making it easier to rank for related content I produce.
Connecting GSC with Surfer can save you hours of keyword research while helping you find many new ideas to write about based on your website's search performance. You can then prioritize these keywords by their relative difficulty or the monthly search volume, both metrics provided by Surfer but not inside GSC.
Read on if you prefer a manual approach and are interested in learning how to use Google Search Console.
How to use Google Search Console reports
Google Search Console provides site owners with several reports for insights on your search analytics ranging from index coverage to structured data. Of course, you won't always need to look at each report to improve your SEO but here are the most common ways to use Google Search Console for your website.
1. Identify your best-performing pages
The Performance report is an excellent place to begin using Google Search Console for your website's search engine optimization, where you can find your topmost pages. The Performance report in GSC measures each page against four metrics or dimensions - total impressions, total clicks, average CTR and average position. You can use any of these to decide how you define your top most pages.
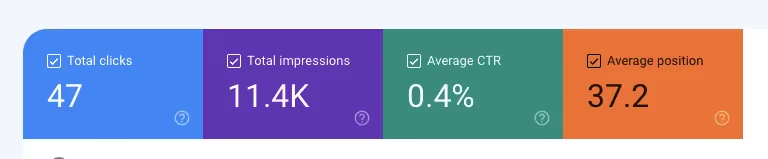
For example, say you are interested in which pages of your website receive the most traffic. This information will help you identify areas in which Google recognizes your website's authority and you can direct your content strategy efforts around them.
To find your most visited pages, sign into GSC and follow these steps.
- Expand the Performance tab on the left panel
- Select Search results
- On the right panel, edit the Date filter and select all the boxes under it
- Select Pages in the tabs under the graph
GSC will show your website's topmost pages based on the four metrics you enabled in the colored boxes.
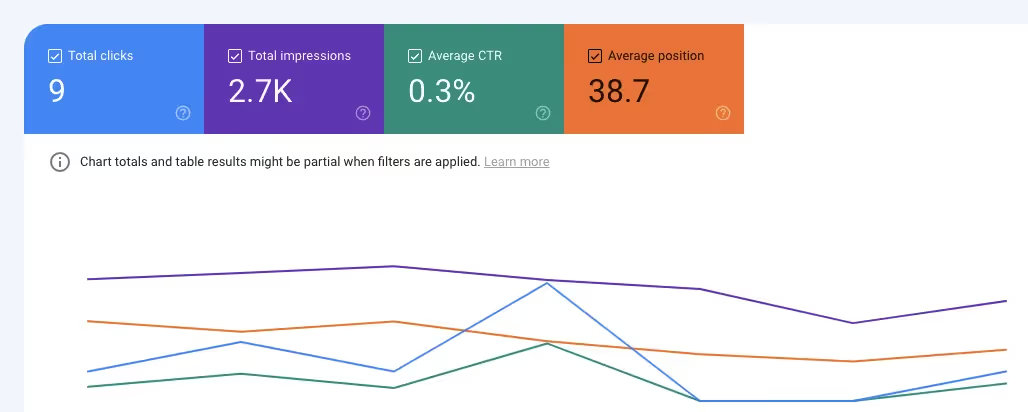
You can then sort them based on a preferred dimension. In this example, to identify the most traffic-heavy pages, I sorted them in descending order by the number of clicks they received in Google search. This shows me the pages my users visit most often through search.
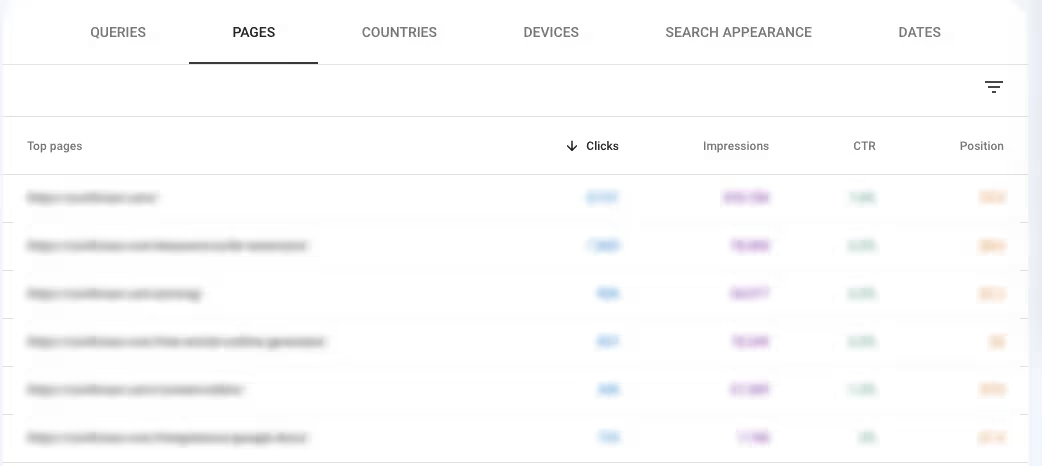
You can see my website's top pages by traffic and now have an overview of which pages contribute to the most visitors.
You may also sort this list by impressions, average click-through rate (CTR) or average ranking position for a deeper investigation. I'll show you how to use these dimensions in the next steps.
2. Identify which pages rank the highest (and lowest)
Google Search Console can help find your website's topmost ranked pages in the search results. Browsing through your highest-ranked pages will give clues to your website authority that you can use to create new content around similar topics.
Besides identifying your best-ranked pages, you can use the average position metric to monitor the ranking progress of a new blog post once it has been published. You can do the same for a page that you have optimized.
To find your best-ranking pages,
- Select Search results in the Performance tab
- Edit your date and device preferences
- Select Average position
- Scroll down and select Pages
- Sort by the Position column in ascending order
You should see the average ranking position for associated pages during your selected timeline under the Position column.
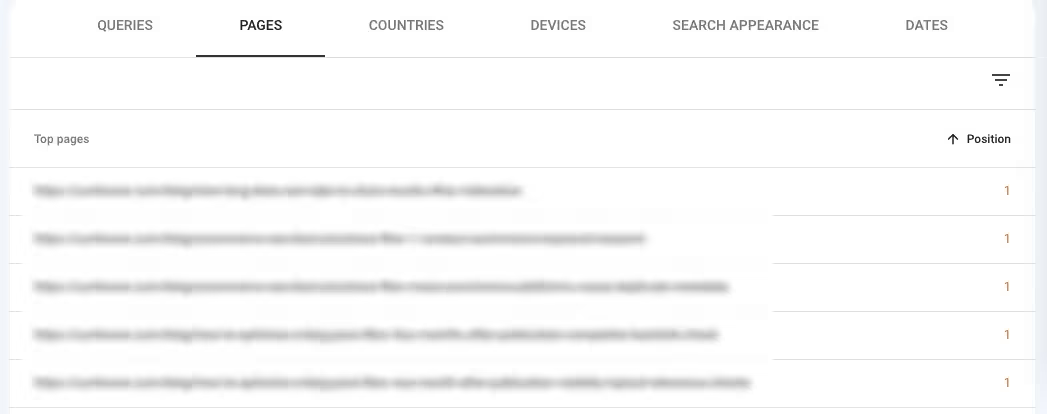
Knowing your worst-ranking pages is also helpful in deciding whether they're worth improving or discarding. To do this, just sort the Position column in descending order.
Surfer Tip: The average position figure is an average of all the positions for every keyword your blog post ranks for in Google. This figure can sometimes be misleading because although you may rank for a secondary term, it may not be your target keyword.
You can track the page's primary keyword ranking that you are targeting. Take a look at secondary keywords but don't be too fussed if they rank in the double digits.
Combined with the average ranking position, the average CTR is a valuable report to identify low-hanging opportunities for underperforming pages.
3. Identify how users interact with your pages in the SERPs
Tracking your pages' click-through rates (CTR) in the SERPs can tell you if your page titles and meta descriptions appear relevant to your target audience. While CTR may not be a direct ranking factor for search engine optimization, it signals the relevancy of your page to certain keywords.
A higher CTR indicates strong relevancy to a search query in your meta descriptions and titles while a weak CTR reveals a lesser match. Follow these steps to track pages with the best search visibility to click ratio in the SERPs.
- Select Search results in the Performance tab
- Edit your date and device preferences
- Select Average CTR
- Scroll down and select Pages
- Sort by the CTR column in descending order
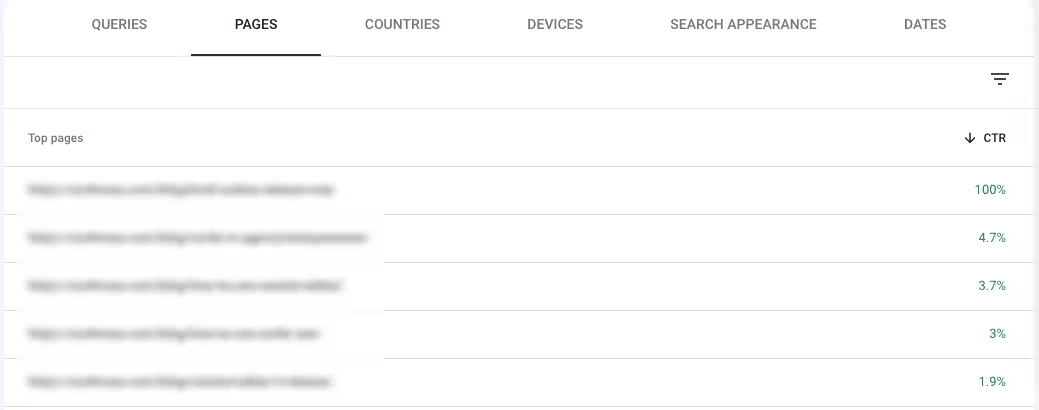
You now have a list of your website's pages based on their click-through performance in the search results. Sort this list in ascending order to find pages with low CTR in the SERPs.
4. Identify pages with the most search visibility
Alongside pages that rank well and receive traffic, it's a good idea to find pages that appear the most frequently in organic search. Sorting your pages by the impressions they receive will show you which of your pages are seen most often in search engines.
To identify pages with the most impressions, follow these steps.
- Select Search results in the Performance tab
- Edit your date and device preferences
- Select Total impressions
- Scroll down and select Pages
- Sort by the Impressions column in descending order
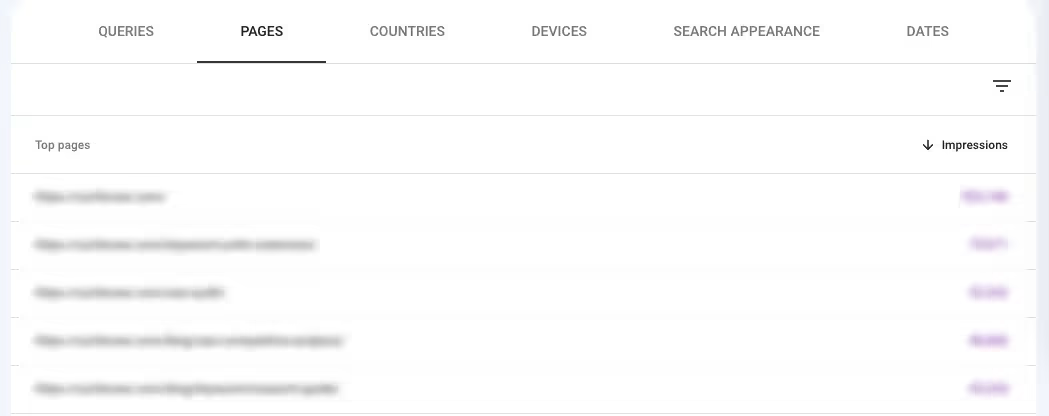
To find pages that receive the lowest impressions, sort the same column in ascending order and you will see your least seen pages in the SERPs.
5. Identify your most important search queries
You can also use Google Search Console to determine the top queries people use to find your pages in Google Search. Identifying a list of your top search queries will give your keyword research strategy a solid foundation to start from.
To find the top most queries for your website, follow these steps.
- Select Search results in the Performance tab
- Edit your date and device preferences
- Select Total Clicks, Total impressions, Average CTR and Average position
- Scroll down and select Queries
You now can sort your top queries by traffic, SERP visibility, click-through rates and average position. Sorting your queries by most clicks and impressions will help you spot search terms that you're ranking well for. Since you're already ranking well in this niche, you can use this information to focus your content strategy on related terms.
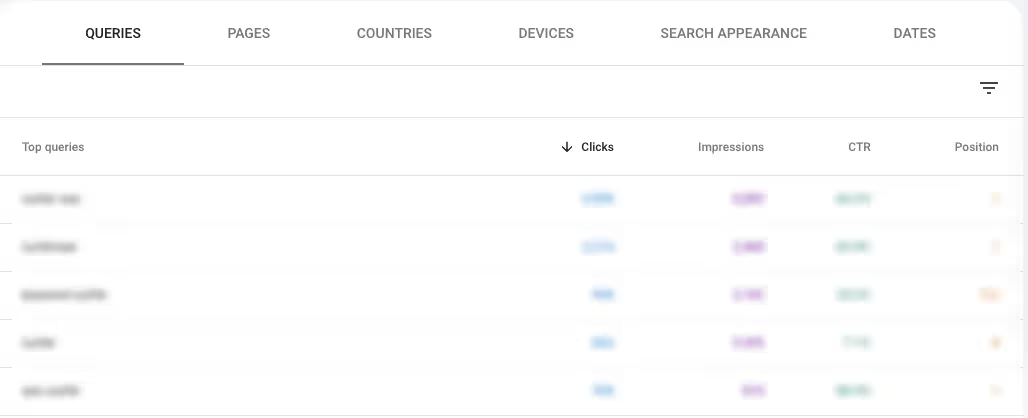
You can also use this report to find queries you need to rank better for, and determine if these are important to your business.
7 Google Search Console hacks for higher rankings
By now, you've learned how to use and interpret your website's data using Search Console's reports. GSC can be a helpful SEO tool as you've seen but to unlock its true potential for SEO, you should consider blending reports. This section will show you a few Google Search Console hacks to uncover actionable data without using keyword research tools.
1. Identify pages with high rankings and visibility but low CTR
We know that the top few positions in the search results receive the most clicks. If you already have pages ranking well, optimizing their CTR for a boost in organic traffic makes sense. But first, you need to find these pages using Google Search Console.
Find pages that are ranking well in the SERPs but have an underperforming click-through rates by following these steps.
- Head to Search results in the Performance tab
- Edit the Search type and Date settings
- Toggle the Average CTR and Average position buttons
- Scroll down and select the filter > Position > Smaller than 5.1 in the Pages tab
- Sort the CTR column in ascending order
Filtering by pages already ranking in the top 5 positions will ensure that you are targeting opportunities that require low effort and can produce quick results before you move on to other pages.
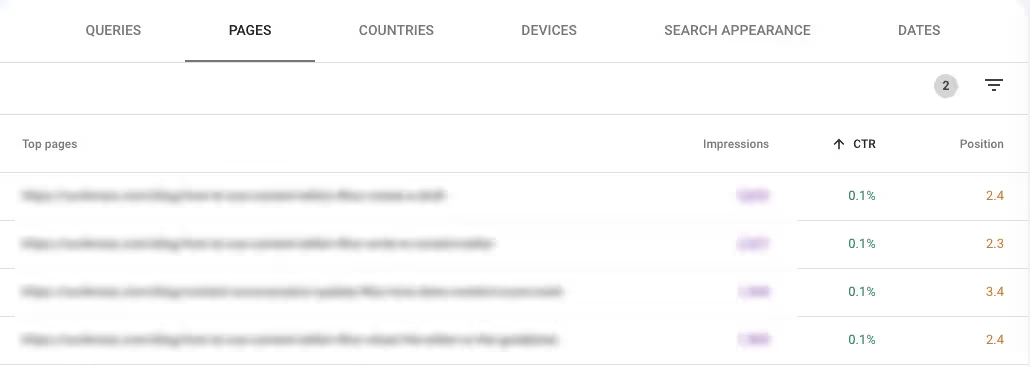
Pick out pages that have high impressions but low CTRs. These have a high search appearance but aren't meeting their full potential for organic search traffic due to low CTR. Optimize the metadata for these pages with relevant titles and descriptions while ensuring your article aligns with the keyword's search intent.
Once you're done with the top 5 positions, change the filter to show you positions smaller than 10.1 and optimize those.
2. Identify underperforming pages with low search visibility
You probably have a few pages that are ranking on page two or three of the search results. Identifying them and analyzing how you can improve their rankings is a good idea. To find pages that have low SERP visibility, do this.
- Head to Search results in the Performance tab
- Edit the Search type and Date settings
- Toggle the Average CTR and Average position buttons
- Scroll down and select the filter > Position > Smaller than 20.1 in the Pages tab
- Sort the Position column in descending order
Browse through the pages in this report and compare them to your competitors ranking in the top positions. Then, verify that you match the search intent and have relevant metadata that appears in the SERPs.
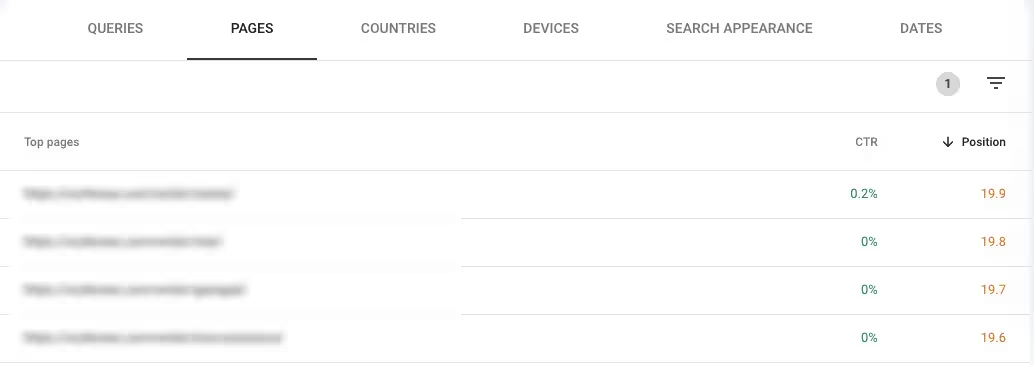
To find pages ranking on page three, change the filter to show you positions smaller than 30.1.
3. Find your most linked to pages
Backlinks are a well-established ranking factor for search engines. Google Search Console can help you find your top linked pages using the Links report. Knowing your heaviest linked pages can guide your link-building strategy.
To find these target pages, head to GSC.
- Select the Links tab in the left panel to open the External links report
- For your most linked to pages, click the Top linked pages tab
- For your highest referring domains, click the Top linking sites tab
- For your most often used anchor text, click the Top linking text tab
For example, I want to find my most linked to pages so I can create similar content around these topics. Filtering this list by Incoming links > greater than 100 shows my website pages with over 100 incoming links. To see only pages on my blog, I can use the Target page > Contains > /blog filter and sort by Incoming links in descending order.
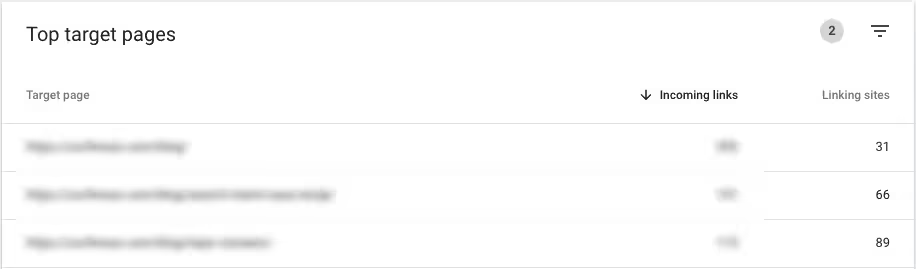
Clicking on any target pages will lead to a report showing referring domains linking to this page.
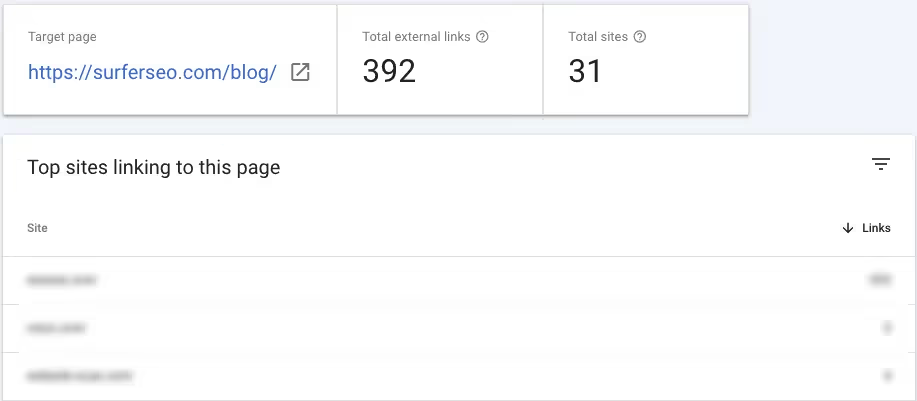
Use this report to identify patterns in content types and topics that attract the most backlinks for your website.
4. Optimize your internal links
Internal links can help communicate essential pages to search engines and impact how new pages are indexed in the SERPs. Therefore, staying on top of your internal linking as your blog grows and you have more pages to manage is especially important.
To generate a report on the internal linking between your website's pages, use the Links report in Search Console. Then, click More in the Internal links report on the dashboard to find your top internally linked pages.
You can use the Target page filter > Contains and enter a partial keyword or URL path if you are looking for internal links pointing to a specific page. For example, I'm only interested in the internal linking of pages on the blog.

Sorting this list in ascending order of internal links shows me the pages on my blog that are either orphaned and thus difficult to find for search engines or blog posts with insufficient internal links.
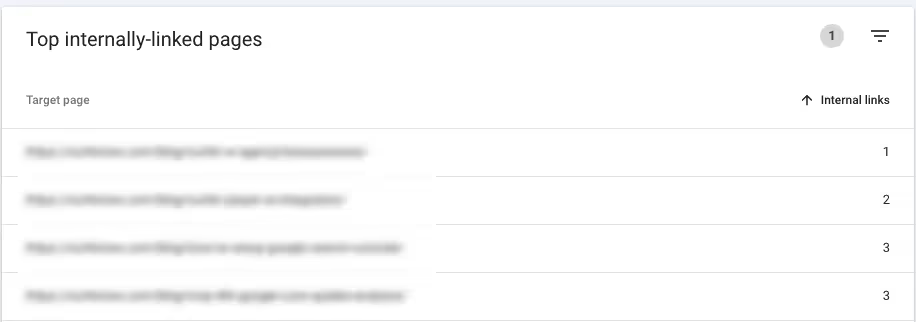
I should increase the number of internal links these pages receive if I consider them important and would like to improve their chances of ranking in the SERPs.
5. Inspect individual URLs
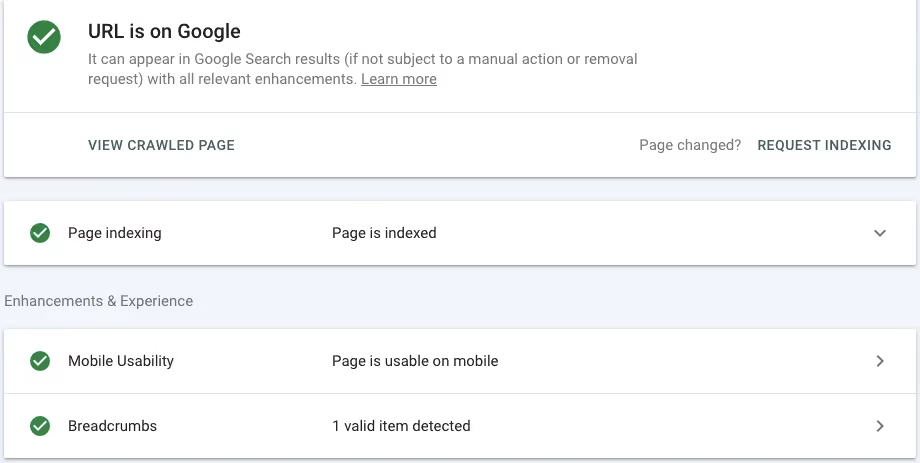
The URL inspection tool in Google Search Console allows you to review the status of a single page. This can be especially useful in diagnosing indexing and canonical issues that creep up occasionally. To use the tool, sign into GSC and enter your complete URL into the search field on the top bar.

Search Console will show you several reports for the page and highlight any issues. If the page appears okay to Google, you'll see all items marked in green.
6. Measure your blog's search performance
Search engine optimization is an ongoing process and not a one-time checklist so it's important to measure the efforts of your blog posts continually. This will help you identify pages that need your attention and find low hanging fruits. Follow these steps to measure your blog's progress.
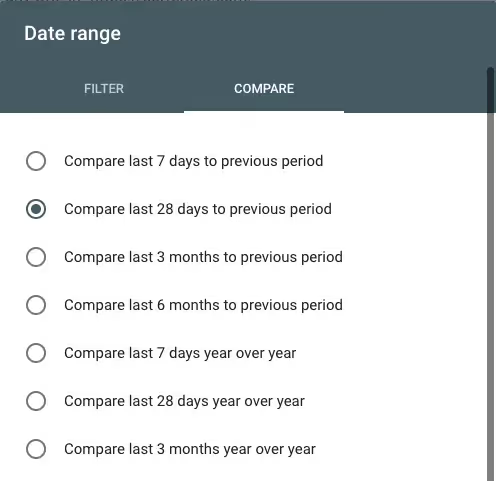
- Head to Search results in the Performance tab
- Click on the Compare tab In the Date settings and select a period and click Apply
Select the dimensions you want to track progress for in the report. For example, I want to uncover changes in traffic to a certain page and queries over the last 28 days by comparing it to the previous period. And so I've edited the Query and Page filter accordingly.
In this case, I'll select Total clicks but I'm also aware that changes in position can significantly affect traffic, so I'll include the Average position metric. Organic traffic visits to this page have dropped along with a minor change in rankings, and the article now rests on the second page of the SERPs.
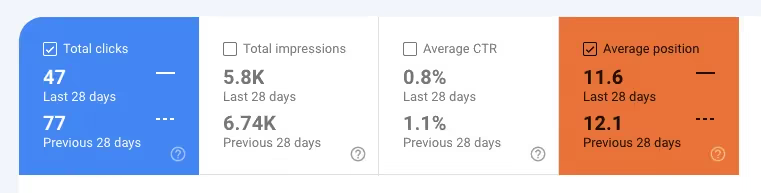
However, there has also been a significant drop in the click-through rate possibly because the article was based on a time sensitive trend that no longer retains its original attention.
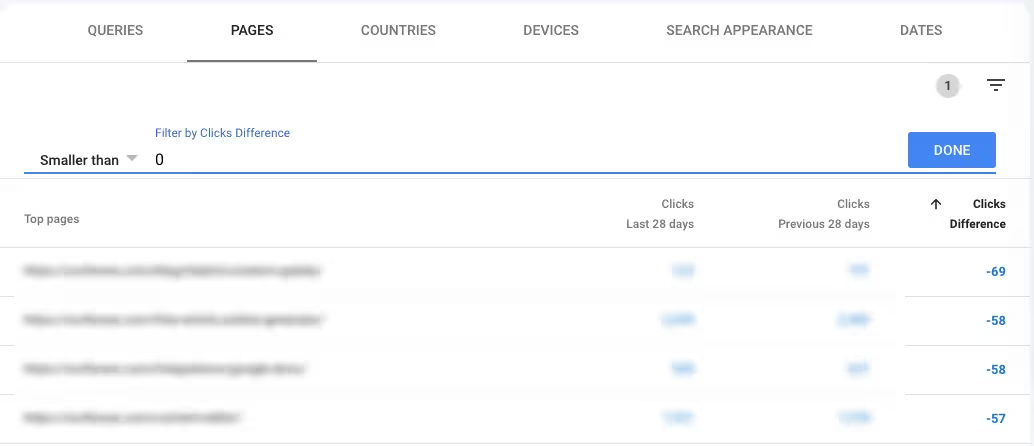
But what if you want to find pages like this that are losing clicks?
In that case, scroll down to the Pages tab, filter by Clicks Difference > Smaller than 0 and sort in ascending order. This will show you pages with the largest decline in clicks on the top so you can address these first.
7. Optimize your crawl budget
It's a good idea to periodically delete pages that don't contribute to your website traffic but are still using up your crawl budget. You're better off replacing these with articles created around relevant keywords with the potential for more traffic.
There's always hesitation to delete webpages you've created but allocating crawl resources to these pages could potentially limit a new page you've published. Follow these steps to find pages with low search appearance and traffic.
- Head to Search results in the Performance tab
- Adjust the Search type and Date filter to at least 6 months
- Toggle Total clicks and Total impressions
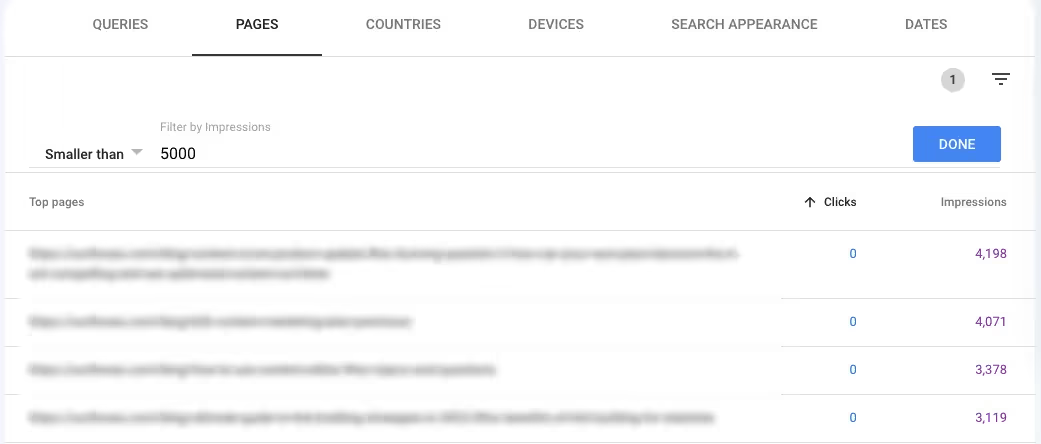
- Scroll and select the filter > Impressions > Smaller than 5000 in the Pages tab
- Sort the Clicks column in ascending order
With these settings, Search Console shows you how many pages receive very little traffic. You can change the Impressions filter to a different figure like 20,000 to find even more pages that you may consider deleting or creating better versions of.
Conclusion
As you've learned, even as a free service, Google Search Console can be an asset when it comes to finding opportunities for your blog's growth. Most site owners make the mistake of using third-party keyword research tools immediately but using GSC to begin your SEO and keyword research efforts can uncover nuggets of opportunities external tools can't.




.avif)
