Predicting results from SEO may be the most challenging aspect of SEO—yet it's often the first thing a client and executives will ask about – "what can we expect?"
When I forecasted Surfer's SEO performance from September 2024 to March 2025 using the method outlined in this guide, the difference was only 10.5% lower than actual clicks.
For a channel with dozens of mystical variables, that's remarkably accurate—and achievable with the right approach.
What you will learn
In this comprehensive guide to forecast SEO, you'll discover
- why even backlink analysis can't fully explain ranking patterns
- how to build realistic forecasts using historical data
- and proven methods to predict future organic traffic that balance both precision and practicality.
Plus I'll link to the SEO forecast template I used.
What is SEO forecasting?
SEO forecasting is a way to predict future website performance based on current and historical SEO data. When implemented well, forecasting can help businesses anticipate traffic patterns, allocate resources efficiently, and establish realistic expectations for organic and business growth.
However, forecasting SEO is trickier than paid marketing channels because organic channels like search engine results are subject to a higher magnitude of factors that you can't control.
Unlike paid channels that allow a framework for forecasting once you have a cost per lead, conversion rate and budget – search engine rankings are influenced by dozens of uncontrollable factors like shifting search trends, algorithm updates, and evolving user behavior patterns.
Let me show you an example with the query "how to raise money for a startup."

Backlinks are widely considered the strongest ranking factor in the SEO community, and several studies have established a correlation between quality backlinks and search engine ranking positions. But there are tons of examples of pages with higher and better backlinks ranking lower than others.
Carta's page ranks on top with 106 unique backlinks.

Followed by the US government's Small Business Administration [1600 unique backlinks], Y Combinator [411 unique backlinks] and Stripe [5 unique backlinks].

Carta's page is likely more relevant and satisfies user intent better than the government's SBA article, which ranks because it is deemed to be highly authoritative (in addition to being relevant, of course).
Just like Youtube, Tik Tok or Instagram can't be forecasted perfectly, estimating SEO growth relies on several factors.
The most important of these have to do with how search engines view your website and its authority.
- Are you trustworthy?
- Is there evidence of historically valuable insights?
- Does your domain have a recognized brand?
- What do others in your space think of you?
And so on.
Sure, you can implement best practices to help your case – this is what SEO is, but predicting SEO is an educated guess with some margin for error.
4 factors that influence SEO forecasts
Even the best-modelled SEO forecasts are subject to various external and internal factors.
When creating SEO forecast estimates, keep these influences in mind to consider how they might cause actual results to differ from your projection.
Search engine algorithm updates
Google and other search engines frequently update their ranking algorithms which can dramatically boost or sink your organic traffic overnight.
Because Google doesn’t fully disclose these updates and their timing in advance, any SEO prediction is inherently uncertain.
However, even if we were told about algorithmic updates, we would have to accept that algorithmic volatility is always going to be a wildcard for SEOs.
Organic search competitors
Search rankings are a zero sum game.
If a competitor expands their SEO efforts, they can achieve the rankings and traffic you had projected for yourself.
Evaluate how much your competitors are investing into their SEO strategy before you can make a confident prediction.
For instance, the credit card space is very competitive. You'd have to consider matching your competitors' link and content velocity before being able to draw numbers on future organic traffic growth in such a niche.
Search trends and behaviour
Search behavior can change due to trends, seasonality, or unforeseen events. A classic example was the pandemic, which led to a surge in certain online searches like “home office setup” and then a normalization afterward.
Shifts in what users want from a query can impact your forecasts. If informational queries give way to transactional ones, your page will decline in rankings.
Just like one of our how-to guides that has given way to tools in the search results, thus reducing click through rates in search results.

Technical SEO
Your website's technical health and performance can influence ranking and how users behave on your site.
Google reports that the likelihood of a visitor leaving your webpage rises by 32% as a page’s load time extends from one second to three seconds – which in turn can negatively affect your rankings.
7 steps to forecast SEO performance from Google Search Console
Since GSC is the most popular source of SEO performance, I'll first break down a simple way to forecast SEO performance using Google Search Console data.
We're going to base our future prediction on past performance from search traffic.
Step 1. Export your data from GSC
- Head to Search Console.
- Go to Performance > Search results
- Adjust the Date range filter to the maximum
- Export your data by clicking on the Export button in the top right.
The longer and more consistent your history, the better it is to forecast SEO traffic —aim for at least 12+ months of clean data.
You should find a new folder in your Downloads area. It looks like this on a Mac.

Step 2. Import your CSV into Google Sheets
- Go to Google Sheets.
- Click File > Import.
- Upload “Dates.csv” from the folder you just downloaded.
- When prompted, choose Import data into a new or existing spreadsheet.

After the import, you will see something like this.

Step 3. Remove Impressions, CTR, and Position columns
We only need Date and Clicks for this simple estimate.
Right-click and delete Columns C-E
Now your sheet should have only A and B.

Step 4. Format the data
To ensure our dates and clicks are recognized correctly, do the following.
- First, move Clicks by 5 columns from column B to column G
- Select the Date column (Column A).
- Click Data > Split text to columns.
- Under “Separator,” choose Custom and type a hyphen (-) or slash (/) depending on your date separator.
- You’ll temporarily get separate columns for day, month, year.
It should look like this.

- Insert a new column or use a formula in empty column D to recombine them with the DATE() function, for example:
=DATE(A2, B2, C2) where A is your year, B month and 2 date.

- Label new column E as “Date[numeric]”
- In E2, type:
=D2 - Press Enter then go to Format > Number > Number.
- Now you should see a numeric “serial date” (e.g., 45710).
- Drag or copy this formula down all rows so each date is converted.
Your sheet should look like this now.

Step 5. Add future rows to forecast
Follow these steps to forecast the next few days or weeks in your SEO forecsating report.
- Arrange your sheet by the latest dates at the bottom by heading to Data > Sort range > Advanced range sorting options
- Copy column D and head to Edit > Paste special > Values only
- At the bottom, drag down column D to add future dates.

- Adjust column E so each future date appears as a numeric value in Column E.
Step 6. Forecast SEO growth
In the corresponding cell in column F, enter:
=FORECAST(corresponding cell of the numeric date for the row to forecast, range of cells for known clicks, range of cells for corresponding numeric dates)
- Press Enter. You should see a numerical predicted Clicks value.
- Drag down to your forecasted date range so each future date gets a forecast.
For example, my formula looks like this in cell F183
=FORECAST(E183,F2:F182,E2:E182)

Adjust your row references.
Step 7. Visualize your SEO estimate
To see your historical and forecasted data on a line chart,
- Highlight columns D and F (including your future forecast rows).
- Give column D a name if you hadn't. I'm going to label it Dates.
- Go to Insert > Chart.
- Select Line Chart.
- Now you’ll see a timeline from your earliest date to your forecast horizon, with your forecast data extending beyond the known historical points.
In the chart below, the arrow points to the forecasted data.

I've simplified the data here which is why the chart is a linear trendline. In practice, you can expect to see something different.
You can find a link to the forecast template below if you would like to take a closer look at the steps I've illustrated.
3 ways to forecast SEO traffic
Of course, estimating your organic traffic from GSC data isn't the only way. You can forecast SEO data from other anaytics tools that you use to monitor SEO performance, including tools like Google Analytics.
When implemented well, forecasting can help you anticipate traffic patterns and establish realistic expectations for organic and business growth.
Here is an overview of 3 additional ways to forecast SEO potential for your web pages.
1. Click-through rate modeling for rankings
Keyword-based forecasting calculates expected page traffic based on your page rank and the volume of search queries it targets.
The major chunk of SEO performance is comprised of the trifecta of keyword rankings, search volume and click through rate.
And so this is the easiest and perhaps most popular way to forecast SEO growth.
In fact, this model is also called keyword growth potential or search volume based forecasting.
Note: This is better for page-level forecasting because it's based on a keyword's individual search volume and ranking.
Click-through rates
A Backlinko study shows that the top organic result in Google receives 27.6% of all clicks, while lower-ranking results receive far fewer clicks.
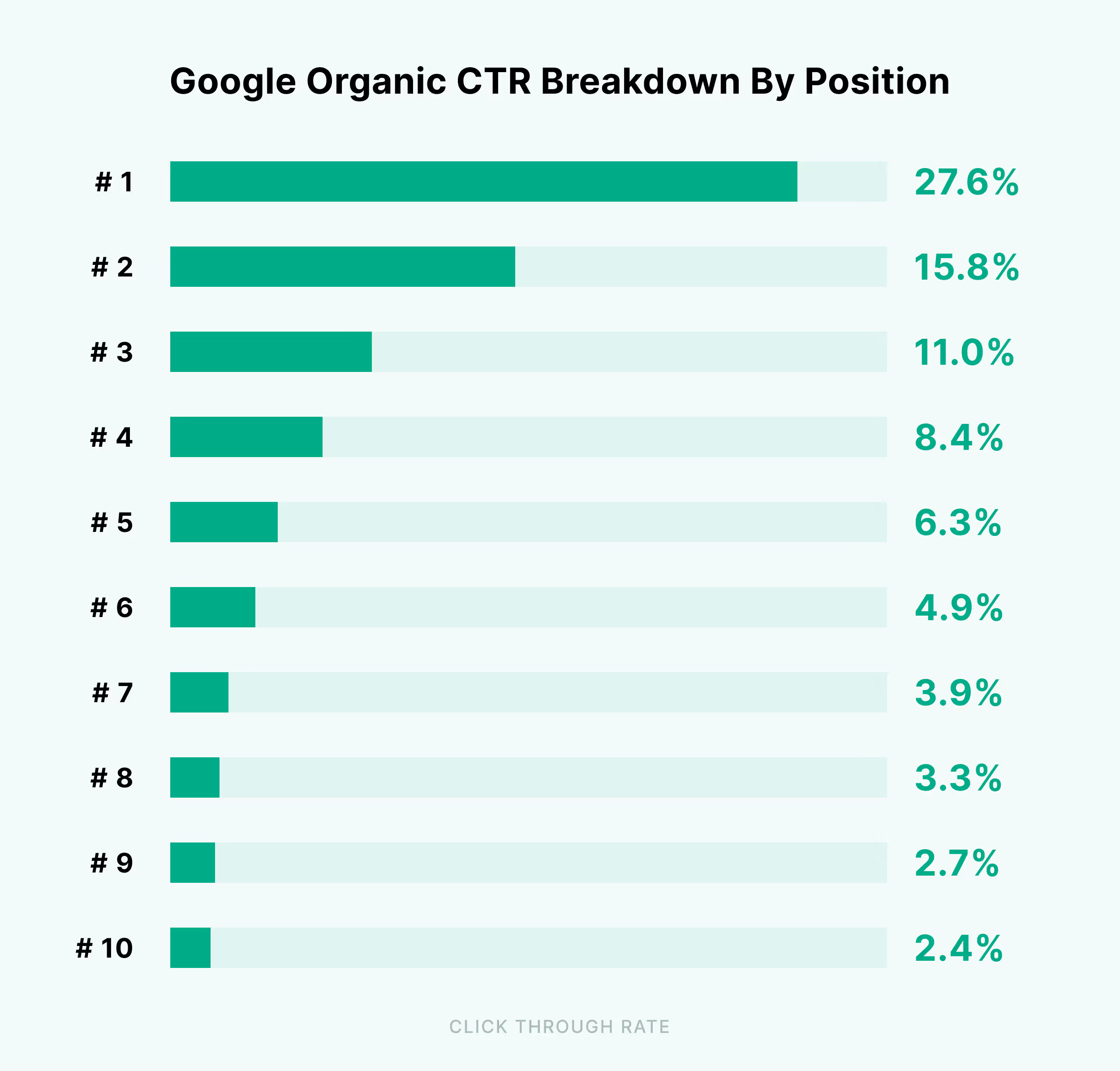
By multiplying the expected CTR by the keyword’s search volume, you can estimate traffic per keyword if you achieve that ranking.
Search volume
If you already have a page targeting your keyword, you can use GSC to find the search volume for that term based on your keyword position.
- Head to the Search results tab and filter your page

- Adjust the custom date range to show 30 days
- Enable the average position tab and look into your queries report.
Here, you'll find which search terms lead to your page. Note your average position for your primary keyword.
For instance, we're ranking in position 8 for our primary term "digital marketing packages."
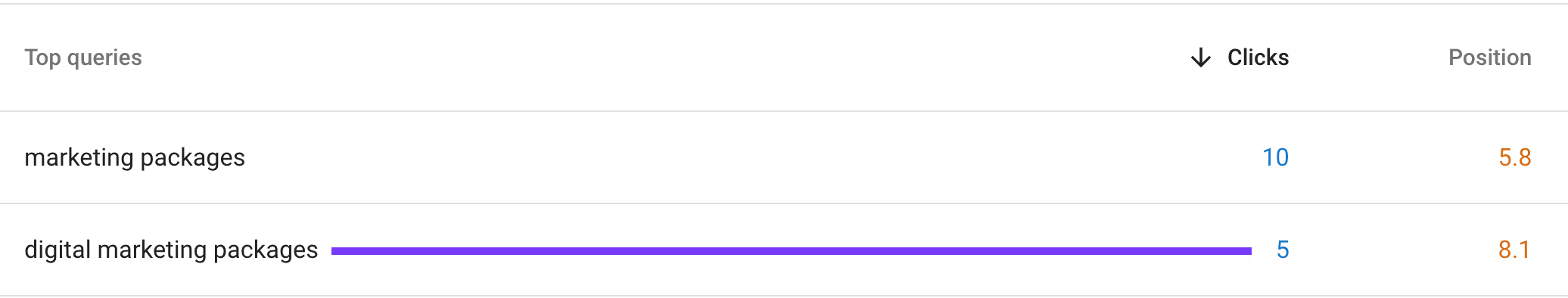
Based on Backlinko's findings, this means we're only getting 3.3% of clicks for this term.
In that case, the total search volume is the number of clicks divided by the percentage of clicks—5 clicks divided by 3.3% for the 8th position.
So "digital marketing packages" has a monthly search volume of 152.
If you don't have existing GSC data, use an SEO tool like Keyword Surfer that shows monthly search volume data.

Now that you have your datapoints, here's how to estimate monthly traffic to your pages.
- Identify a relevant keyword
- Note its monthly search volume and assess how well you could rank for it (consider current ranking or realistic improvements).
- Then apply a formula: Projected Traffic = Search Volume × Expected CTR for your anticipated ranking.
For example, if a keyword gets 10,000 searches a month and you're ranking in position 5, you may estimate roughly 6.3% of those searches as visits, translating to 630 monthly clicks.
This is a simple place to start forecasting organic traffic, but several variables can come into play in practice.
CTR can differ by query type, brand presence, and your snippet’s appeal.
For instance, instead of assuming Backlinko's 11% CTR at position 3 for all keywords, analyze your GSC performance report to see what CTR you actually get when you rank in the 3rd position.
You may find that your site’s position 3 CTR is 25% on informational queries but 40% on branded queries – insights that you can plug into forecasting.
Another challenge with this model is that pages often rank for many terms, not just one, so an ideal forecast will sum the traffic from multiple keywords per page.
Inspite of its limitations, it's a a simple starting point to evaluate potential traffic for new content, or to prioritize updates to existing pages.
2. Analyze seasonality trends
This method accounts for seasonal variations and projected growth trends to provide more nuanced predictions.
For example, if a website's average monthly traffic is 10,000 visitors, and December historically shows a seasonal growth of +30%, the projected December traffic would be 13,000 visitors. This approach is particularly valuable for businesses with pronounced seasonal fluctuations in demand.
Insufficient historical information may overlook important cyclical trends that can impact future performance.
Look for recurring peaks or dips (e.g. holiday spikes or annual events) and perform year-over-year, or month-to-month comparisons.
Surfer's blog for instance sees a seasonal dip during the December holidays, and pulls back up in January.

An e-commerce site might see traffic jump every November due to Black Friday sales. Knowing this, you’d forecast a similar uplift next November and allocate more resources ahead of that peak.
It’s also important to distinguish between one-time events and sustained trends. Use tools like Google Trends to verify if a keyword’s popularity is rising, falling, or stable.

The key is to base your forecast on long-term trends. If searches for your products increased by 30% last spring and this spring, it’s reasonable to project a comparable rise next spring, adjusting for any anomalies.
Also consider keyword trend data: if a keyword’s search volume has been growing, factor that growth rate into your projections.
Marketing analytics is a deep study, and you can continue to perfect your forecasting model for days on end.
3. Extrapolate historical data
The foundation of a strong SEO forecast is historical performance data, which provides insights into past trends and patterns that can predict future projections.
SEO forecasts are only as good as your historical data.
You'll need to have cleaned data in one place in a friendly format.
- Format: You’ll want a time series with columns like,

Ensure consistent frequency: Make sure you have a regular time interval (e.g., monthly). If you have daily data, you can resample/aggregate.
Remove any outliers unrelated to normal seasonality or consider smoothing or excluding them.
Plot your traffic over time and look for:
- Trend: Is traffic generally going up or down?
- Seasonality: Do you see recurring patterns (e.g., every December traffic dips)?
- Level shifts: Did you have site migrations, big SEO changes, or algorithm updates?
Applying statistical models (e.g. linear regression or moving averages) to this data can project future performance while accounting for regular seasonal fluctuations.
A few popular forecasting methods are,
- ARIMA / SARIMA (Seasonal ARIMA):
- Good for modeling autocorrelation and seasonality directly in the data.
- Use pmdarima or statsmodels in Python.
- Prophet (by Facebook/Meta):
- User-friendly, handles seasonality/holidays relatively easily.
- Often a good choice if you have strong weekly/annual patterns.
- Holt-Winters (Exponential Smoothing):
- Another classic for trend + seasonality.
How to forecast SEO revenue
Once you have a traffic forecast, it's a good idea to use these findings to predict how that traffic turns into business results.
Here are 2 methods to forecasting revenue from SEO.
1. Conversion rate forecasting
Start with your conversion rate – what percentage of organic visitors complete your desired goal (purchase, sign-up, etc.)
Use a historical conversion data from Google Analytics or a similar measurement platform.
If your website’s organic conversion rate has been 2% consistently, you can apply that to future traffic volumes.
The basic formula is straightforward,
Expected conversions = Projected organic traffic × Conversion rate
For example, if you anticipate an extra 3,000 monthly visitors from improved SEO rankings and your site converts 5% of visitors, that’s 0.05 × 3,000 = 150 new conversions (leads or sales) you can forecast.
It’s wise to segment your conversion rate by action.
You might have one conversion rate for e-commerce purchases and another for newsletter signups, for instance.
After forecasting the number of conversions, attach an average value per conversion to estimate revenue.
150 sales at an average $100 order would mean $15,000 of additional revenue.
If your site’s goal is lead generation, you might assign a monetary value to each lead (perhaps based on historical lead-to-sale rates or known lifetime value per lead).
Using conversion rate forecasting ties your traffic projections to real dollars, allowing you to demonstrate how SEO growth might impact the bottom line.
2. Customer lifetime value estimation
Not every customer acquired via SEO is a one-off transaction.
Especially for businesses with recurring sales or loyal customers, the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV or LTV) of organic visitors is an important factor. CLV is the total revenue a customer is expected to generate over their entire relationship with your business
When forecasting SEO revenue with CLV, you’re not just looking at the immediate sale from an organic visitor, but also their potential repeat purchases or retention value.
For example, imagine your average customer spends $2000 with you over 2 years, and about 10% of organic leads eventually become customers.
In that case, each new lead has an expected value of $2000 × 0.10 = $200
Apply your projected conversions from SEO along with your historical customer retention rate or repeat purchase frequency.
If out of 100 new customers from SEO, on average 30 make a second purchase within a year, you’d add that additional revenue into your forecast.
The CLV perspective often shows that the true value of SEO is higher than just the first sale.
By highlighting lifetime value, solopreneurs and enterprises alike can better justify SEO investments – “This SEO-driven sale is worth $X over 2 years, not just the initial $Y purchase.”
If your SEO strategy brings in customers who stick around, make sure your forecasting model captures that compounding revenue.
Download our forecasting SEO template
Ready to build your own SEO forecast?
Make your own copy and you can change the numbers and see the formulas.
Download our free SEO Forecasting Template that implements the techniques covered in this guide—from step 1 to 7 of the basic GSC data forecasting projections.
Forecasting SEO ROI
Any forecast should ultimately address the return on investment (ROI) of SEO efforts.
Forecasting your SEO's ROI compares the projected cost of your SEO activities to the revenue you expect SEO to generate.
The formula is simple,
SEO ROI (%) = (Additional SEO Revenue – Additional SEO Costs) ÷ Additional SEO Costs × 100
Tally your SEO costs for the forecast period – including content creation, SEO tools, agencies, link-building expenses, and your own time or team salary allocated to SEO.
Then use your forecasted SEO revenue (from increased conversions, CLV, etc.) to calculate the ROI percentage.
For example, if over the next quarter you plan to spend $5,000 on SEO and expect roughly $20,000 in sales from organic traffic, the projected ROI is (20k – 5k) / 5k × 100 = 300%
Your SEO ROI in this case is $4 return for every $1 spent.
ROI forecasting helps decision-making: you can compare it to other marketing channels or use it to ensure your SEO plan makes financial sense.
Forecasting ROI over an extended period, say 12 months can capture cumulative benefits. For instance, content created today might generate traffic for years with only maintenance costs increasing ROI over time.
Keep in mind that SEO is a long-term play, so ROI can continue to build up gradually.
How accurate is SEO forecasting?
Forecasting SEO results can vary due to search engine ranking factors, which can cause actual results to differ from an estimate.
While researching this article, I asked Perplexity what it thinks of SEO forecasting.
SEO forecasting exists in a space between science and art, offering valuable predictive power while contending with inherent uncertainties.
– Perplexity AI
It's a bit heavy on the AI verbiage, but not wholly incorrect.
To test the simple forecasting method that we discussed earlier, I forecasted our SEO performance from September 2024 to March 2025 based on historical data between November 2023 and August 2024.
Here's what that looks like.

In red are actual clicks versus the forecasted traffic in blue.
The estimated average daily clicks are 10.5% lower than actual clicks from Google during the period of September 2024 and March 2025.
Which I think is a fairly decent forecast.
The challenge of SEO forecasting lies in the dynamic nature of search algorithms and user behavior, which introduce variables that are difficult to quantify.
And so a variance of 10-30% is to be expected, even with more advanced modeling.
You'll be pressed to find an experienced SEO professional who will willingly forecast exact traffic predictions, and for good reason.
Search constantly evolves as Google launches core algorithm updates, new SERP features like Google's AI-powered search results emerge overnight, and external factors impact traffic, conversions, and revenue in ways no spreadsheet can anticipate.
Besides these, Google doesn't help matters.
Take the example of Google's helpful advice on creating content.

Like my therapist, Google's heart is in the right place, but how exactly do I use this advice?
If you read the page, there are several pointers to help you assess what makes good content in the eyes of Google, but you can appreciate why it makes forecasting SEO difficult.
There is no standard for helpful content, regardless of how much we are told that Google likes well-written, useful articles.
In reality, simple calculations are enough to estimate organic search results. What you're doing is projecting historical trends while accounting for seasonality and trends.
Despite these challenges, forecasts remain crucial for business planning and decision-making. Organizations increasingly demand answers to the question,
"If I were to invest x, what would my return be?"
To address these demands while managing expectations, SEOs must temper forecasting methodologies with realism, relying on historical patterns and projected growth opportunities.
What I therefore like to do, is make conservative forecasts within an upper and lower range that I'm fairly confident we'll hit. We're not betting the company on a 17.6% rise in organic clicks next quarter.
This avoids disappointment and any business decisions don't have to be revised to accommodate for a lack of results.
If anything, we almost always surpass our forecasted goals for SEO.
As my colleague at Surfer notes,
"The best SEO forecasts acknowledge their limitations. I tell website owners we're building educated predictions, not guarantees.
When we forecast with 10-30% variance ranges rather than exact numbers, we actually hit our targets 90% of the time."
— Kristavja Caci, SEO Content Marketer at Surfer
While SEO forecasting can't account for every external factor, it can come close when built on solid data and a clear strategy.
9 data sources for SEO forecasting
Reliable forecasting depends on comprehensive and accurate data sources. Here are 9 data sources to help predict SEO traffic, rankings, and revenue.
1. Google Search Console
Because Google is the only trustworthy source of its own data, it should be your number 1 source to pull data when making an SEO forecast, for maximum accuracy.
If you can, extract information using the Google Search Console API instead of the standard export feature to get a longer history instead of the typical trailing 16-month report.
2. Google Analytics (Free)
Same reason to use GA4 as a data source.
- Tracks user behavior, conversion rates, and traffic trends.
- Helps forecast revenue based on past organic conversion rates.
- Provides segmentation by traffic source, location, and device type for more precise forecasting.
3. SEOmonitor
- Specifically designed for SEO forecasting.
- Uses historical ranking data and machine learning to predict traffic gains.
- Provides scenario modeling for different ranking outcomes.
4. Surfer
While Surfer doesn't offer a forecasting feature, you can set up Goals in its Reports tool to fix targets for search volume and keyword rankings.

Setting a goal for your SEO campaigs will help you measure progress against how much traffic you forecasted.

You can also use Surfer's estimates for monthly organic search volume when calculating your forecasted clicks.

5. Rank Ranger
- Helps forecasts keyword ranking trends
- Benchmarks your site’s performance against competitors for clearer growth projections.
- Advanced, customizable reports ideal for client communication and performance tracking.
6. Searchmetrics
- Predicts how your SEO strategy might impact search visibility and rankings over time.
- In-depth benchmarking against competitor websites to identify growth opportunities.
- Analyzes content effectiveness, forecasting traffic potential based on keyword research.
7. Prophet by Meta
- Not an SEO tool per se but offers advanced, open-source forecasting
- Allows integration with Python and Excel, perfect for tailored SEO forecasting models.
- Capable of capturing complex seasonalities and trends, improving forecast accuracy significantly.
8. Ahrefs
- Offers keyword volume trends, ranking difficulty, and organic traffic estimates.
- No forecasting feature but helps analyze competitor performance.
- Provides backlink data, which is useful for understanding ranking potential.
9. SEMrush
- Features SEO forecasting tools that estimate organic traffic growth.
- Includes competitive analysis to benchmark against competitors.
- Provides traffic potential analysis for targeted keywords.
You can also use Google Trends or BrightEdge and Conductor, if you're doing enterprise SEO.
This is not an exhaustive list, and you don't need one. Even the most sophisticated SEO tools have limitations in their data collection and analysis capabilities.
Estimating SEO forecasts typically requires at least two years of data to understand and account for seasonality in traffic patterns.
Takeaways
- SEO forecasting is a crucial process for businesses to predict future website traffic and search engine rankings.
- By understanding the benefits and challenges of SEO forecasting, businesses can make informed decisions about resource allocation and marketing strategies.
- By using essential metrics, data collection, and SEO forecasting techniques, businesses can create reliable forecasts with a margin for error.
- By following best practices and avoiding common mistakes, businesses can optimize their SEO efforts and achieve better return on investment (ROI) for marketing efforts.




