So how do search engines work? They crawl the internet to collect information, scouring their index to find and rank relevant content that is then indexed, evaluated, and displayed to satisfy a user’s query.
Several factors influence a search’s results. These include the relevance of visual or text elements to the query and the item’s up-to-dateness. Additionally, the search engine’s assessment of a site’s strength plays a role.
Understanding how search engines work allows you to optimize your site’s online visibility and ensure your content ranks high.
After all, it’s all about driving traffic to your site and ensuring user engagement.
What you will learn
- What search engines are and what they aim to achieve
- The mechanism behind crawling, indexing, and serving results
- How Google determines what sites to serve to users
- How to optimize your site to show up at the top of search results
What are search engines?
Search engines are systems designed to search for and find relevant information on the internet in response to a user’s query or keyword.
These systems use web crawlers to browse the internet systematically.
Search engine algorithms match the user’s query with indexed content to deliver relevant results.
While Google is the most widely used, it is important to also consider other search engines like Bing and Yahoo for a comprehensive online presence.
Below, we’ll introduce some of the world’s most popular search engines and mention their distinctive features.
Google: Google is a powerful search engine that offers extensive search capabilities and personalized results.

Google hold 91.04% of the search engine market share.

Bing: Bing is a search engine from Microsoft known for its strong image search capabilities and integration with various Microsoft services.

Yahoo: Provides a comprehensive search experience with added features like news, email services, and finance information.

DuckDuckGo: Puts user privacy first by not tracking searches or personalizing results.

Brave Search: Prioritizes user privacy and independence from major tech ecosystems.

Yandex: Dominant in Russia, it is known for effectively handling Russian language queries.

Baidu: Designed to handle Chinese language searches. It is the most popular search engine in China.

How Google search works
Google search works by using web crawlers to discover and index web pages, then analyzing and ranking them based on relevance, quality, and user intent to deliver the most pertinent results. This is how search engines rank URLs to deliver the most pertinent results.
Nevertheless, all search engines work the same way. They go through the following three stages to serve search results:
- Crawling: Google uses web crawlers, called “Googlebots,” to discover and fetch web pages across the internet.
- Indexing: Involves analyzing text, images, and video files. These are then processed and added to Google’s massive index, which is a huge database of web content.
- Serving results: Google presents the top results to the user as a search engine results page (SERP).
These stages allow Google to deliver relevant and high-quality search results within fractions of a second.
What is the aim of search engines?
Every search engine aims to help users search for information and present them with results that match their query.
The goal is to deliver the most relevant and high-quality results.
Search engines work to establish trust and credibility by consistently providing accurate and reliable results.
Users, therefore, tend to repeatedly return to the same platform and even recommend it to others. This allows a particular search engine to grow its market share on the Internet.
How do search engines make money?
Search engines make most of their money through advertising, particularly the pay-per-click (PPC) model.
Some private search engines make money through affiliate links, contextual ads, and donations.
Search engine pages display organic and paid information. Organic results are naturally generated based on the search query and the relevance of the content to the query.
Paid results, on the other hand, are ads that show up at the top and bottom of pages. These ads are typically labeled as "Sponsored" or "Ad" and are paid for by the advertiser.

With the PPC advertising revenue model, advertisers pay every time a user clicks on their ad. Advertisers bid on keywords or phrases that relate to the products or services they provide. When a user enters one of those keywords in the search bar, the search engine displays ads that match the query.
This model is profitable for search engines because it allows them to charge for each ad click.

Additionally, search engines can generate revenue through other means. Here are some examples:
- Display advertising: Charging sponsors for text and image ads on search engine results pages.
- Paid inclusion: Charging websites for inclusion in targeted search engines or directories.
- Habit reports: Selling marketing data on consumer habits or using it for targeted advertising.
- Selling market insights and data analytics services: Offering bespoke market insights to businesses based on user queries, trends, and online behaviour.
How search engine crawling works
Crawling is a process used by search engine crawlers (known also as spiders, robots, and search engine bots), like Googlebot, to index the web.
These web crawlers scan the internet to find new or updated pages to catalogue text, images, and videos.
This web content discovery is used to update databases with relevant and recent information.
The process begins with URL discovery, where Google locates new or updated website pages to add to its list of indexed pages. This continuous search ensures an up-to-date search index.
Googlebot discovers new pages primarily by following links from already-known pages. Or you can submit an XML sitemap via Google Search Console, which lists URLs you want the search engine crawler to index.

When crawling your website, google allocates it a "crawl budget".
Googlebot might stop looking at your site if it finds too many inappropriate URLs for the search index. This can happen if your site has a lot of low-quality content, duplicate pages, or irrelevant URLs.
Effectively managing your crawl budget ensures that Googlebot focuses on the most important pages of your site, improving your site's indexing and visibility.
Here are some tips to effectively manage your crawl budget:
Prioritize high-quality content: Ensure that your most important pages are easily accessible to crawlers. Use internal linking to highlight key pages and make sure they are not buried deep within your site structure.
Limit duplicate content: Duplicate content can waste your crawl budget. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page, and avoid creating multiple URLs with similar content.
Optimize URL parameters: Excessive URL parameters can create unnecessary variations of the same page. Use parameter handling tools in Google Search Console to specify how parameters should be treated.
Regularly update your sitemap: A well-maintained XML sitemap helps Googlebot find and prioritize the most important pages on your site. Update your sitemap regularly to reflect any changes or additions.
Use Robots.txt wisely: Use the robots.txt file to block crawlers from accessing low-value or non-essential pages, such as admin pages, login pages, or duplicate content.
Monitor crawl errors: Regularly check Google Search Console for crawl errors and fix any issues promptly. This ensures that Googlebot can efficiently crawl your site without encountering obstacles.
Reduce server response time: A slow server can limit the number of pages Googlebot can crawl. Optimize your server performance to ensure quick response times, allowing more pages to be crawled within your crawl budget.
How search engines index pages
After discovering new content, Google analyzes it and stores the information in its vast Google search index database.
Indexing involves processing and understanding the content, including:
- Title elements
- Alt attributes
- Text
- Images
- Videos
- and other media.
Google aims to understand the context and meaning of a page's content; not just simple keyword matching.
Advanced natural language processing techniques are used to understand the subject matter, sentiment, and entities in the text.
You can use Google’s Natural Language API demo before submitting a new article. This will clarify how Google will understand your content. Categories indicate the subject matter of your article.

High content quality can secure a page's inclusion and ranking in the Google index.
Pages with thin, low-quality, or duplicated content may be excluded or given lower priority.
To determine duplicate pages, Google clusters pages with similar content. The most representative web page is selected as the canonical page.
This system ensures that the results are relevant and not overloaded with duplicate content.
Only the most useful pages based on the user's context are listed.
Here’s how you can check how many pages from your website are in Google's index.
Use “site operator” followed by “domain name,” like this: site:surferseo.com.

How search engines serve results
Search engines serve results by scouring their index databases to find and present the most relevant and high-quality content tailored to the user's query, location, language, and device.
To establish the relevancy of a search result, the search engine identifies the:
- User's location
- Language
- Device
After that, search engines work at assessing each page's content, including its purpose, quality, and relevance to the query.
Additionally, Google evaluates:
- Expertise
- Authority
- Trustworthiness of the content creator
- User interaction with the page
For example, if you search for "pizza places," Google will present you with listings near your location. Similarly, if your browser is set to Spanish, the results will favour Spanish-language content.

Google's ranking process is programmatic. It does not accept payments or other considerations for higher placement.
This ensures that search results are unbiased and focused on providing the best possible experience for users.
Showing up on Google search engine results
By understanding how search engines evaluate page and serve results, you can take the right measures to have your pages show up on search engine results.
Content relevance
Content relevance means providing information that matches the user’s search intent.
Searchers want to find content that directly answers their questions or meets their needs.
One easy way to establish intent is to look at the search results for the query. You should start by analyzing the top 10 organic results and SERP features.
By recognizing the types of content that appear in the results, you can identify the primary intent behind the search query.
Look for features like featured snippets, “People Also Ask” questions and local packs. They can indicate the type of content that is most useful for the search query.
Additionally, analyze the top-ranking pages to understand what they are doing well and what gaps they might have.
The analysis will help you understand search intent. You can then create content that better meets the target audience's needs.
Let's establish the intent behind “Best noise canceling headphones.”
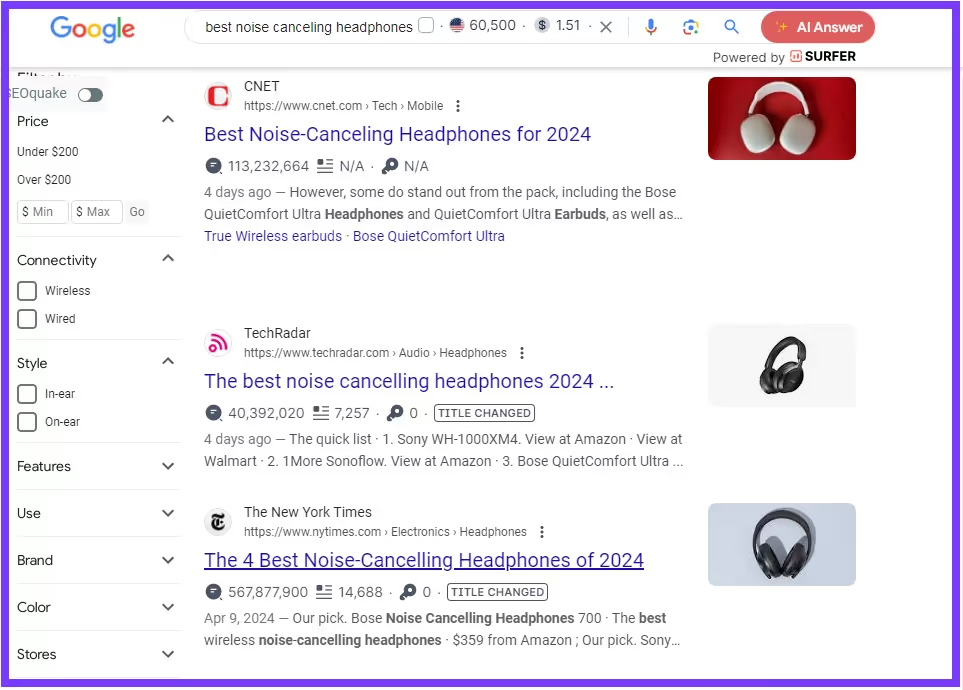
It is enough to open the first three articles. We find lists of headphones with a short description, price, and where they can be bought.
Our conclusion should be that Google is classifying a commercial intent to the keyword.
But how does Google find the most relevant content?
Google establishes content relevance through a combination of signals, including:
- If keywords from the search query are present in the content, such as in headings, body text, and other sections.
- Seeing if relevant terms are present in the content.
- Ensuring that the content avoids keyword stuffing and is not excessively repetitive.
- Using aggregated data from user interactions with search results to refine its relevance.
The search algorithms prioritize helpful and trustworthy content.
Here's how you can use Surfer to assess the relevance of the content and ensure you are sending the right signal to search engines.
In the Content Editor you will find a list of relevant terms, including both primary and secondary keywords. These are known as entities that inform Google on what your page is about.
There you can also see how often they should appear in your content.

If you're using Surfer AI to create your content, then it will be already optimized for these specific terms.
You can add these terms manually or use Surfer's Auto Optimize to do it for you.

The freshness of information
Search engine algorithms prioritize delivering the latest and most relevant content to meet user expectations when they look for current information on evolving or time-sensitive topics.
Google favours newer pages for queries related to breaking news, trending topics, and annual events.
Subjects that have frequent updates, like technology or medical advice, are included in this category.
Search engines also try to determine the user's query intent—whether they are seeking recent information or not. If the search behavior or context implies a need for the freshest content, more recent pages are prioritized in the rankings.

Additionally, Google considers social signals like a surge in shares, mentions, and new inbound links (link velocity) as signs that content is timely and relevant. This positively influences search engine rankings.
Regularly updating and revising existing content can boost its rankings even for less time-sensitive topics.
Adding new data, links, and information signals to Google that the page remains relevant and useful.
Consistently publishing fresh, updated content aligned with search intents helps improve a website's visibility in search results.
Backlinks
Backlinks are hyperlinks from one website to another. These links can be in text (anchor text), inside an image, or via a button that directs visitors to another site.
Links can connect several websites and allow users and search engines to discover and evaluate content across different domains.
They play a decisive role in Search Engine Optimization (SEO) as they serve as endorsements and votes of confidence.
Backlinks signal the quality and credibility of the linked-to site to search engines like Google.
The impact of backlinks on search rankings is significant.
Google values authoritative, contextually relevant links from authoritative sites.
Such links carry more weight in search engine evaluations than low-quality or unrelated links.
For instance, a backlink from a renowned technology blog to a tech startup's website would be more impactful for search rankings than a link from a cooking blog.
In addition, Google's algorithms are designed to recognize and discount backlinks that are part of a scheme to manipulate rankings. This approach ensures that backlinks genuinely represent a vote of confidence.
Page speed
A website's page loading time directly impacts user experience by affecting how quickly they can access the content they need.
Users will likely bounce from a website that doesn't load quickly. In fact, the probability of a bounce almost triples if a page takes longer than three seconds to load.

Google considers page speed a search ranking factor.
Websites that load quickly are considered more user-friendly and are more likely to rank higher in search results.
To analyze and improve page speed you can use Google PageSpeed Insights.

Mobile-friendliness
Google's mobile-first indexing policy demands websites take this issue seriously, as it directly impacts how sites are indexed and ranked.
One of the best ways to ensure mobile-friendliness is to implement responsive design on your site.
Responsive design adapts content based on screen size for a consistent experience, while dedicated mobile sites are tailored for mobile devices, optimizing content and navigation.
PageSpeed Insights also provides detailed analysis and recommendations to improve mobile performance. It focuses on:
- Server response time
- Network requests
- And content delivery.
Key Takeaways
- Search engines like Google use web crawlers to discover, index, and rank web pages based on relevance and quality.
- Web crawlers systematically browse the internet to find new or updated pages to add to the search engine's index.
- After crawling, the content is processed and stored in a vast database, where it is analyzed for context and meaning.
- Search engines deliver results by matching the user's query with the most relevant and high-quality indexed content.
- Content must match the user's search intent, with signals like keywords, user interactions, and context playing a crucial role.
- Search engines prioritize up-to-date content, especially for time-sensitive topics. Regular updates can improve rankings.
- High-quality backlinks from authoritative sites signal credibility and improve search rankings.
- Faster loading times enhance user experience and are a significant ranking factor for search engines.
- Responsive design and mobile optimization are essential for better indexing and ranking due to Google's mobile-first policy.
- Search engines primarily make money through advertising models like PPC, where advertisers pay for each click on their ads.
Conclusion
Understanding how search engines work is crucial for optimizing your website and improving its visibility.
By focusing on content relevance, freshness, quality backlinks, page speed, and mobile-friendliness, you can enhance your site's ranking and drive more traffic.
Remember, search engines aim to provide users with the most relevant and high-quality results, so aligning your strategies with these goals will ensure better performance and user engagement.
Keep these key factors in mind, and you'll be well on your way to mastering search engine optimization.



